
Figure 2 from Choroid Plexus Papilloma of Foramen of Luschka Semantic Scholar
The lateral aperture of the fourth ventricle or foramen of Luschka (after anatomist Hubert von Luschka) [1] is an opening at the lateral extremity of either lateral recess of the fourth ventricle opening anteriorly [2] into (sources differ) the pontine cistern [2] / lateral cerebellomedullary cistern [3] at cerebellopontine angle. [3]

Microsurgical anatomy of the foramen of Luschka in the cerebellopontine angle, and its vascular
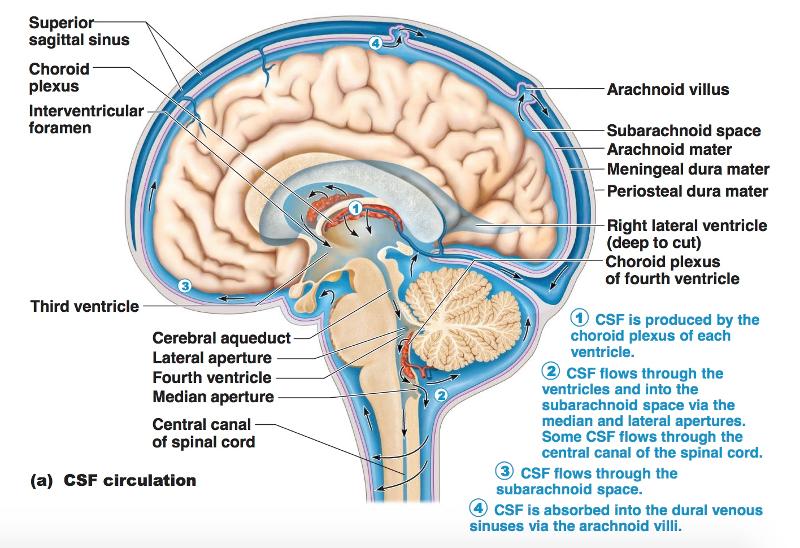
The CSF finally leaves the fourth ventricle through the foramen of Magendie and the foramina of Luschka to reach the subarachnoid space surrounding the brain. Each lateral ventricle lies within a cerebral hemisphere.
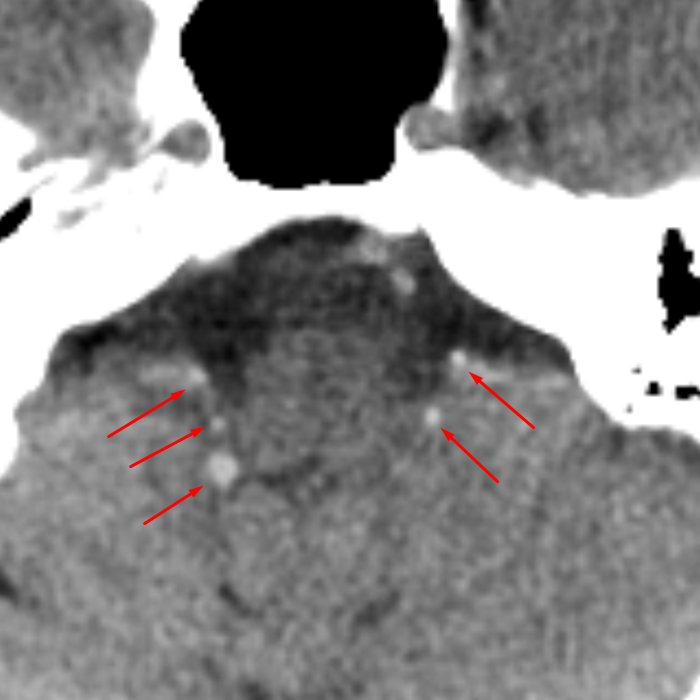
Choroid Plexus in Foramina of Luschka
Bochdalek's flower basket is the eponymous name for the incidental finding of protrusion of the choroid plexus through the foramina of Luschka. This is a relatively common finding.

Figure 1 from Choroid plexus papillomas of the foramen of Luschka MR appearance. Semantic Scholar
The foramina of Luschka (FOL) are counted as a considerable microsurgical corridor to the floor of the fourth ventricle. Understanding the patency of FOL can potentially improve tetraventricular microsurgical and neuroendoscopic approaches.

28 Endoscopic Magendie and Luschka Foraminoplasty Neupsy Key
Hydrocephalus can be classified as either "obstructive and non-obstructive" or "non-communicating and communicating" based on the presence of a flow circulation abnormality inside or outside the ventricular system.

(PDF) Microsurgical anatomy of the foramen of Luschka in the cerebellopontine angle, and its
The uncovertebral joints, also known as the joints of Luschka or neurocentral joints, are the four pairs of plane synovial joints between the vertebrae C3-C7. They are found lateral and anterior to the intervertebral foramina, on each side of the relevant intervertebral discs.

VENTRICLES AND THE CEREBROSPINAL FLUID Neupsy Key
The fluid (cerebrospinal fluid) is produced in the ventricular system of the brain. There are four such hollow spaces in the brain that house cerebrospinal fluid (CSF): two lateral ventricles, a third ventricle and a fourth ventricle. This article will look at the structure of this system and how it helps the brain. Contents Choroid plexus

Organization of the ventricular system of the brain. The brain... Download Scientific Diagram
The foramen of Luschka is a natural aperture between the fourth ventricle and the subarachnoid space at the cerebellopontine angle (CPA). The microsurgical anatomy of the foramen and the related neurovascular structures is well described in the literature. 1, 2,.
What is the position of foramen of magendie, foramen magnum and luschka?
Background: The German Anatomist Hubert Von Luschka first described the foramina of Luschka (FOL) in 1855 as lateral holes in the fourth ventricle.By his discovery, he refuted previous beliefs about the lateral recess as blind ends of the fourth ventricle, proving the continuity of the ventricular system with the central canal of the spinal cord.
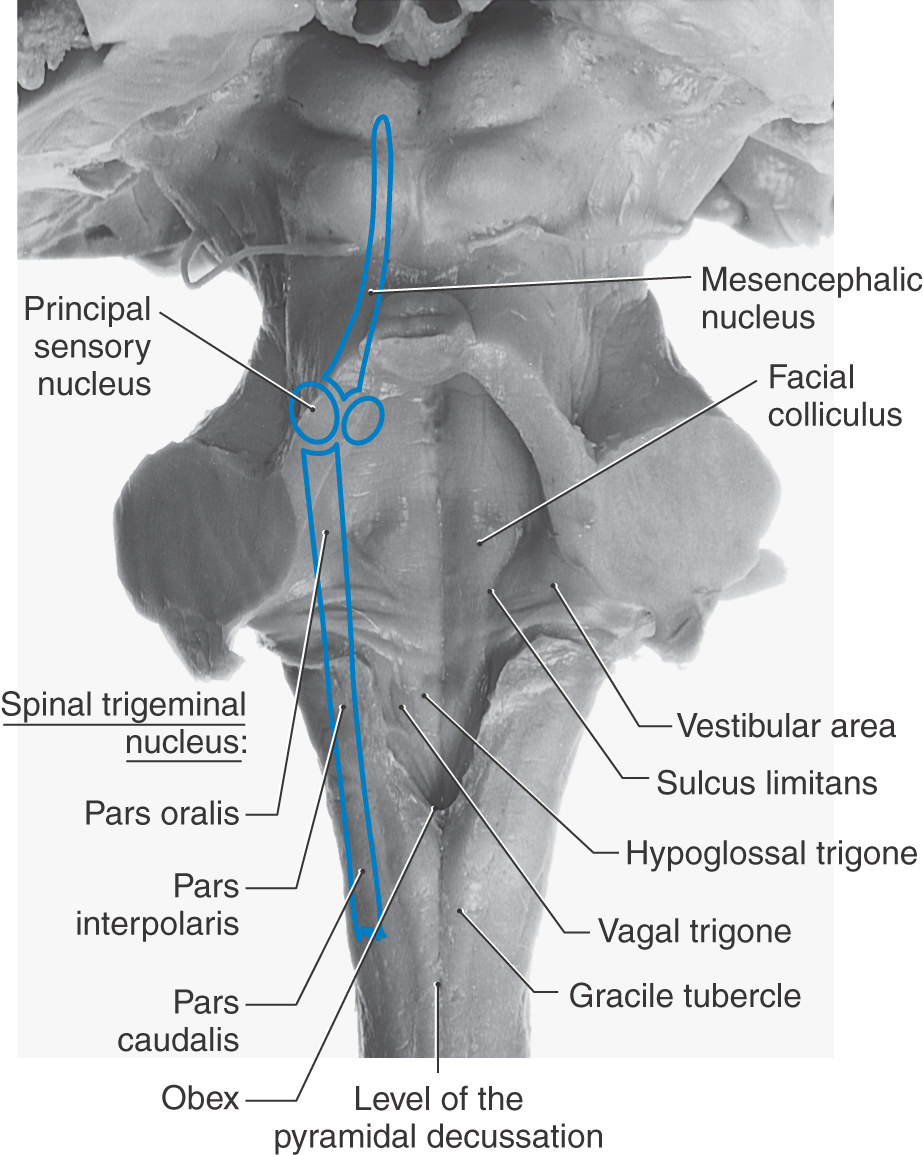
An Overview of the Brainstem Clinical Gate
transmit choroid plexus through the foramina of Luschka into the adjacent subarachnoid spaces. The fastigium is a triangular, blind-ending, dorsal midline outpouching that points towards the cerebellar vermis. The fourth ventricle gradually narrows as it courses inferiorly, forming the obex.
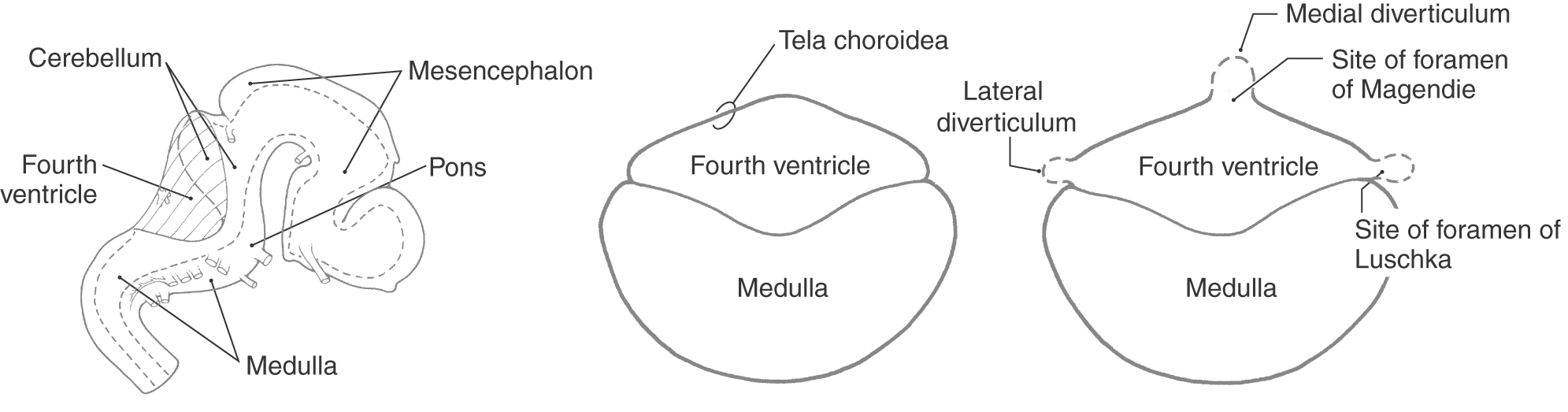
The Ventricles, Choroid Plexus, and Cerebrospinal Fluid Clinical Gate
Background: The foramen of Luschka is a natural aperture between the fourth ventricle and the subarachnoid space at the cerebellopontine angle (CPA). Membranous closure of this foramen is referred.
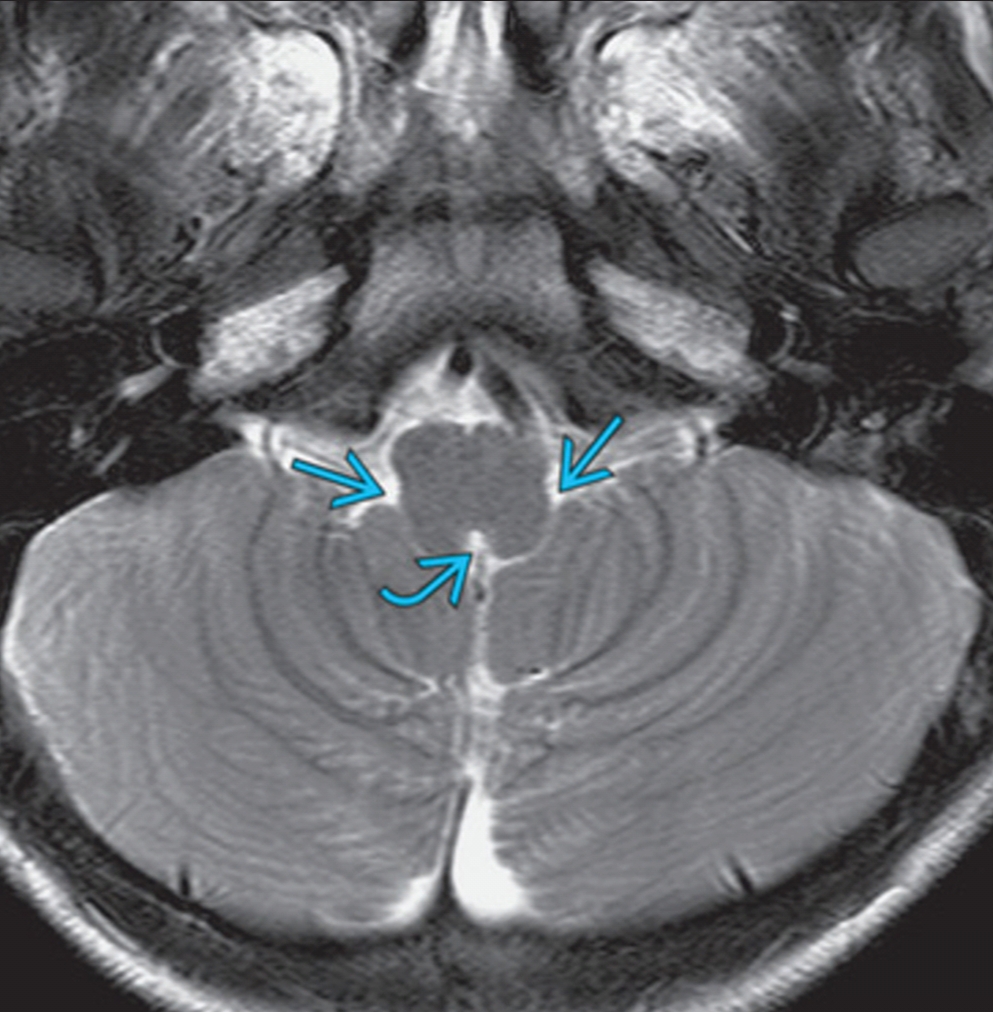
ventricular system overview Brain Imaging
lateral foramina of Luschka: Also known as the lateral aperture, an opening in each lateral extremity of the fourth ventricle of the human brain that provides a conduit for cerebrospinal fluid to flow from the brain's ventricular system into the subarachnoid space. EXAMPLES.

Microsurgical anatomy of the foramen of Luschka in the cerebellopontine angle, and its vascular
Gender: Female. ct. Bilateral linear calcification in the 4th ventricle extending laterally though the foramina of Luschka, represent choroid plexus calcification. This can mimic interventricular hemorrhage. Marked choroid plexus calcification in the lateral ventricles. No acute infarct. Old bilateral insular ischemic changes.

Microsurgical anatomy around the foramen of Luschka in relation to intraoperative recording of
Jaspreet Johal, Phillip Barrett Paulk, Peter C. Oakes, Rod J. Oskouian, Marios Loukas & R. Shane Tubbs 948 Accesses 6 Citations Explore all metrics Abstract Purpose The purpose of this review is to comprehensively review the foramina of Luschka in regard to their discovery, embryology, anatomy, and surgical relevance. Methods

Image result for foramen of monro and luschka Cerebrospinal Fluid, Occipital, Spinal Cord
The lateral apertures (of Luschka) (also known as the foramina of Luschka) are two of the foramina in the ventricular system and link the fourth ventricle to the cerebellopontine cistern. Together with the median aperture (of Magendie) they comprise two of the three sites that CSF can leave the fourth ventricle and enter the subarachnoid space.
Chapter 12 The CNS (Brain and Spinal Cord) Flashcards Easy Notecards
6 PMID: 29339320 DOI: 10.1016/j.wneu.2018.01.037 The foramen of Luschka is a natural aperture between the fourth ventricle and the subarachnoid space at the cerebellopontine angle. Membranous closure of this foramen is referred to as primary obstruction.